-
2016.02.06 Max Velocity Turbine
- 2019.10.23 Google vient de réussir un exploit quantique
- 2019.10.18 Allemagne: La charge de soutien aux énergies renouvelables électriques
- 2019.03.25 France crossed the course of "Gray Day"
- 2018.08.03 Creation of ethanol from spruce wood
- 2017.10.29 L'énergie Solaire Mobile
- 2016.02.06 Max Velocity Turbine
- 2015.05.15 Eliminer le frottement entre deux surfaces
- 2014.12.02 Hydroliennes : GDF Suez-Alstom et EDF-DCNS lauréats de l'appel d'offre
- 2014.10.29 Rossi Congratulates Carl-Oscar Gullström on Theoretical LENR Paper
- 2014.09.11 Fast, clean, green, cheap: Is this our hydrogen fuelled future?
- 2014.07.26 New splitting technique for producing hydrogen fuel
- 2014.03.07 Here is the room where the Internet was born
- 2014.03.06 Is Earth's infrared radiation a potential energy source ?
- 2014.03.04 Lockheed had struck a deal with Ocean Power Technologies
- 2013.11.27 Lenrs and the Future of Energy
- 2013.11.08 UE: huit métaux stratégiques sous risque de pénurie
- 2013.08.12 Elton Musk unveils the Hyperloop project
- 2013.05.21 Indication of anomalous heat energy production
- 2013.04.24 Free Energy launches first solar assisted air conditioning
- 2013.03.04 "Artificial leaf" makes fuel from sunlight
- 2012.12.27 De l'eau de mer pour chauffer des habitations
- 2012.11.19 La méthanisation prend de l'ampleur
- 2012.11.09 La fusion nucléaire dans un appartement
- 2012.10.31 Parabole solaire Dish Stirling
- 2012.10.07 Revolutionary New Solar Power Technology
- 2012.09.25 Fine particles in Europe exceed WHO values
- 2012.09.17 Physicists make discovery about temperature in convection
- 2012.08.28 1000 MW de solaire photovoltaïque au Chili
- 2012.08.28 L'Allemagne ajoute 15,2 MW photovoltaïque à son parc
- 2012.07.27 The Asian Tiger Moskito will bite you
- 2012.08.03 Death of Martin Fleischmann
- 2012.07.20 Siemens to offer 1.3 billion euros for Ansaldo Energia
- 2012.07.13 Site traffic
- 2012.07.04 Higgs boson announcement live
- 2012.06.17 EU Water and Power Ltd was born
- 2012.06.11 Micro-hydroélectricité au Kenya
- 2012.06.05 New fuel cell in line for European award
- 2012.05.04 Association CIEL announces his goal
- 2012.03.19 Alstom inaugurates the largest offshore wind turbine in the world
- 2012.03.19 Le premier parc solaire de Haute Loire inauguré
- 2012.03.13 Terres rares : offensive contre la Chine à l'OMC
- 2012.01.25 Centrifugal force and Free Energy
- 2012.01.17 Alstom et SSE Ren. vont développer l'énergie de la houle
- 2011.12.30 Et pourquoi pas des éoliennes volantes
- 2011.11.07 Alstom projette de construire des éoliennes offshore
- 2011.09.11 L'ASN a reçu les rapports préliminaires ECS des exploitants
- 2011.07.01 Centrale hydroélectrique de pompage turbinage
- 2011.03.31 Nucléaire : les Agences de Sureté nationales et internationales
- 2011.03.17 Une nouvelle usine marémotrice en Ecosse
- 2011.01.19 Projet éolien offshore Français
- 2010.04.10 Un moteur surunitaire est en service en France
- 2010.11.18 Un complexe énergétique solaire géant à Ouarzazate
- 2010.09.27 Alstom s'affirme comme fournisseur leader du programme nucléaire chinois
- 2010.09.07 Alstom signe un contrat éolien au Royaume Uni
- 2010.06.12 Quelle électricité renouvelable en France ?
- 2010.05.20 Alstom fait son entrée sur le marché de l'énergie solaire
- 2010.05.17 Une vague géante fait couler la centrale de production d'énergie
- 2010.04.12 Pollution par les PCB
- 2010.03.24 Bill Gates promeut le nucléaire pour les pauvres
- 2010.03.23 La photosynthèse artificielle pour produire de l'énergie
- 2010.02.28 EDF investit dans une centrale solaire géante à Toul
- 2010.01.13 STEORN prouve la surunité
- 2010.02.10 Nouvelle centrale photovoltaïque en PACA
- 2010.01.04 La plus haute tour du monde inaugurée
- 2009.12.07 Un nouveau moteur brésilien surunitaire?
- 2009.11.13 Focus : Copenhague 2009
- 2009.11.04 Alstom et Schlumberger collaborent sur la techologie CO²
- 2009.11.04 Le débat sur le pic pétrolier serait inutile
- 2009.11.12 Solaire Citoyen
- 2009.09.21 Chine: 300 GW d'énergie électrique en 2020
- 2009.09.18 Rassemblement européen à Colmar
- 2009.09.09 Accident grave sur une barrage en Sibérie
- 2009.07.23 Les piles à combustible
- 2008.10.17 EDF choisit OpenHydro pour des hydroliennes
- 2008.09.08 - Le solaire photovoltaïque
- 2007.04.03 Une centrale solaire à tour en Espagne
- 2007.10.22 La production d'énergie pourrait décliner avant 2040
- Edition
-
2016.02.06 Max Velocity Turbine
Advancing the wind and water turbine industry
Currently, only the outer 30% of a typical wind turbine blade produces any meaningful torque and involves less than 5% of the total disk area. Aerodynamic efficiency is utilized but no attempt is made to divert or accelerate the air at all. In other words, the drag side of the equation is completely ignored.

5 times more blades' surface hit by the wind
It is anticipated that this new blade design will operate in winds eight times slower than the wind needed by other turbines! This means that the MV Turbine technology will produce more electricity and for more hours of the day.
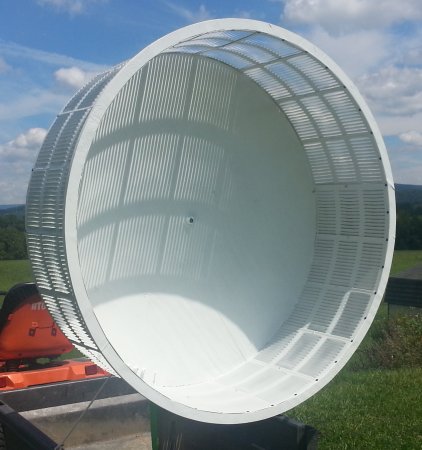

Currently the wind industry designs aerodynamic efficiency like an aircraft propeller. This results in long thin blades that utilize less than 3% of the available air flow effectively, when measuring the tip area versus total area. Most of the air passes through unaffected. Only the tip of the blade maximizes leverage. In the illustration to the right, all the flow impacts the back plate causing it to accelerate and divert through the turbine blades. These blades are mounted around the perimeter at both the maximum point of leverage and highest flow velocity. As a result all the flow is then utilized for the maximum energy conversion.
In addition it should be stated that conventional turbines frequently kill birds by blade impact. With this turbine design the birds will see it as a solid object and therefore fly around it, not attempt to fly through it as they do with conventional wind generators.
Concept of bladed rotor
See more at following links : http://world-harmony.com/max-velocity-turbine/
